Cable vehicles are definitely helpful for transporting cargo up steep mountain slopes, however what if you wish to do the identical kind of factor on a a lot smaller scale? Effectively, you would strive utilizing a tiny new light-powered robotic, which is cable of carrying objects up skinny mid-air tracks.
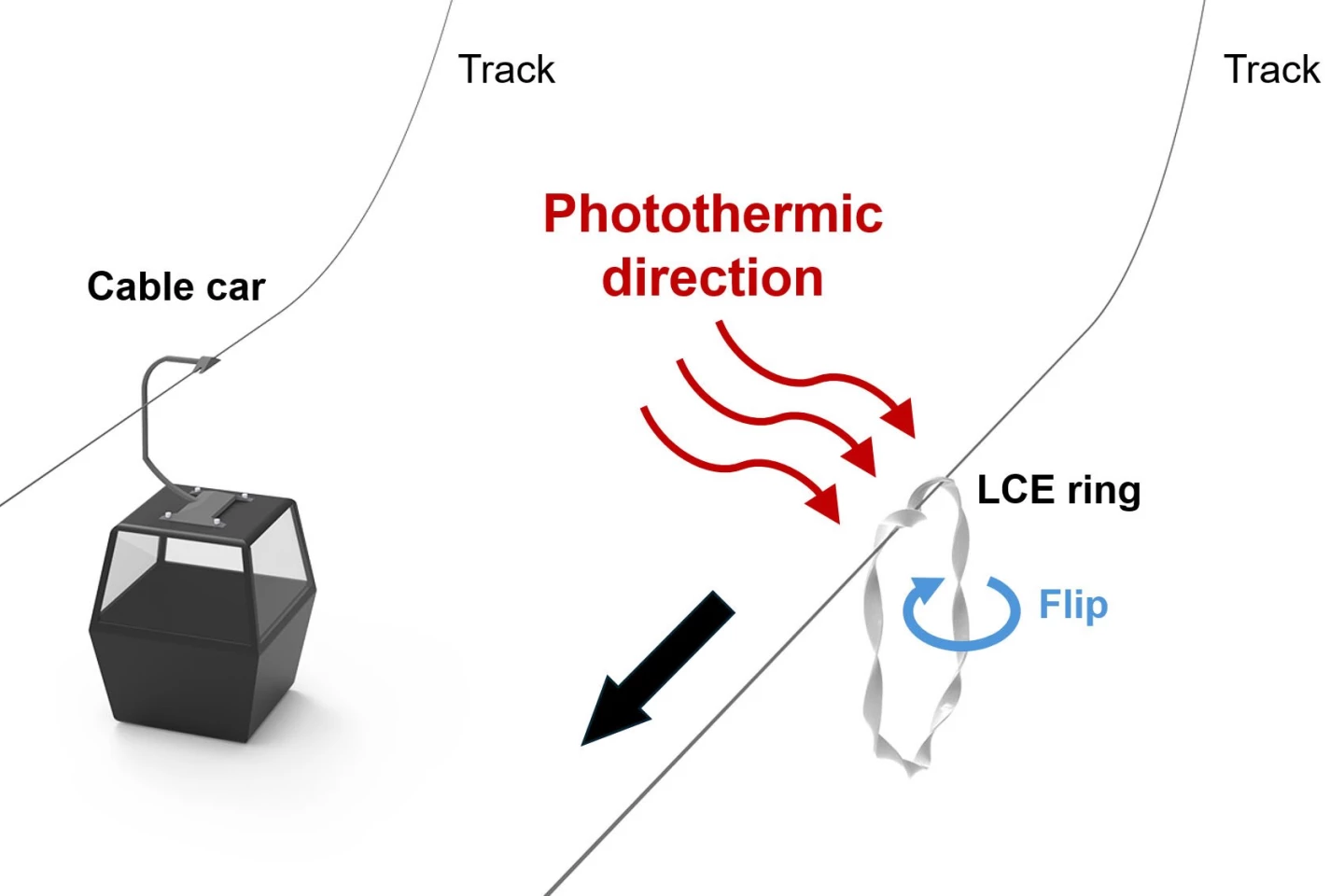
Developed by Assoc. Prof. Jie Yin and colleagues at North Carolina State College, the “robotic” is definitely only a looped ribbon of light-sensitive liquid crystal elastomer. That ribbon has quite a few twists in it, making it look a bit like a spiraled rotini noodle that is been fashioned into a hoop.
When the robotic is suspended on a horizontal or diagonal-sloping monitor – resembling a wire or thread – it is positioned in order that the monitor runs via two or three consecutive twists within the ribbon. The remainder of the bot hangs under the monitor. The cargo merchandise in flip hangs from the underside of the looped robotic.
Upon being uncovered to infrared mild emitted from an overhead supply, the part of elastomer that is situated closest to that supply (the highest part, via which the monitor runs) responds by contracting. Because it contracts it additionally rolls, forming an auger-like screw-drive mechanism.
That mechanism not solely pulls the robotic alongside the monitor, it additionally repeatedly strikes light-exposed elastomer away from the sunshine supply whereas concurrently drawing light-disadvantaged elastomer up into the sunshine. On this style, the bot can indefinitely make its method alongside the monitor so long as the sunshine supply persists.
Fangji Qi, NC State College
In lab exams carried out to date, completely different variations of the robotic have been in a position to transfer alongside each straight and curved tracks ranging in thickness from the width of a human hair to the width of a consuming straw. The bots might additionally make their method over monitor obstacles resembling knots, climb slopes as steep as 80 levels, and carry cargo over 12 instances their very own weight.
“We’re now occupied with particular functions for this know-how, in addition to adapting the comfortable robots to reply to inputs apart from infrared mild,” says Yin. “For instance, creating a comfortable ring robotic that operates in daylight or in response to different exterior vitality sources.”
A paper on the analysis was just lately revealed within the journal Superior Science. You’ll be able to see the robotic in motion, within the video under.
Aerial tram-like autonomous comfortable ring robotic
Supply: North Carolina State College



